Microcontrollers Improve Power
[09-13 17:03:33] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8436次
文章摘要:Abstract: High-speed microcontrollers are widely used in portable equipment. With the proper use of a power management mode, the designer can optimize the life of batteries used in today's new systems. This application note looks at ways to reduce power consumption by choosing efficient clock so
Microcontrollers Improve Power,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comAbstract: High-speed microcontrollers are widely used in portable equipment. With the proper use of a power management mode, the designer can optimize the life of batteries used in today's new systems. This application note looks at ways to reduce power consumption by choosing efficient clock source and clock speed, the use of stop mode, idle mode and burst mode. The Maxim High-Speed Microcontroller and Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontroller families provide the user with advanced features for battery-backed applications.
Portable products continue to advance in features and capabilities. Customers are demanding more performance out of their products, which requires greater computing power. At the same time, they want products with less power consumption. At the heart of these competing demands is the microcontroller, which is typically one of the largest power consumers in portable instruments.
Low-power processors exist, they are often limited in performance. The high-speed microcontroller family from Maxim is a good compromise of power and performance. It is based on the 8051 architecture, one of the most popular microcontrollers in the world. Designers prize its ease of use, rich I/O structure, and wide acceptance. Its prevalence has carried over into the portable arena, where it has found a home in many applications.
This article addresses approaches to minimizing power consumption using 8051 controllers, with emphasis on new architectural improvements that can extend the battery life of high-performance 8051-based designs. Integrating peripherals on-chip and selecting the proper clock source are discussed as ways to reduce power consumption. Software techniques for power conservation are presented, as well as a method of reducing power consumption in systems that use Stop mode.
Clock Speed
The most important factor in determining power consumption in any microcontroller design is the system clock speed. The power consumption of complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices is directly proportional to clock speed. It follows, then, that it is beneficial from a power standpoint to run a processor at the slowest speed possible.Figure 1 shows a typical power curve for a generic 8051 microcontroller, a relationship known to all portable system designers. In general, the current vs. frequency characteristic is linear, with a DC offset. This quiescent current is caused by static circuitry on-chip, such as comparators, operational amplifiers, etc. While this number is typically small (< 1mA), it is a constant drain that needs to be considered.
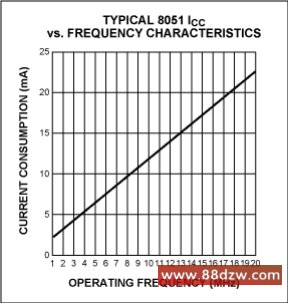
Figure 1. Typical power curve for generic 8051 microcontroller.
Any power-conscious design will attempt to run as slowly as possible. Determination of the minimum system frequency, and hence minimum power consumption, is dependent on a number of factors, including desired performance and interrupt latency. Whatever criteria are used, however, the end goal is the same: match the operating frequency of the device as closely as possible to the requirements of the application.
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] 下一页
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
《Microcontrollers Improve Power》相关文章
- › MICRF501 300~500 MHz收发器
- › MICRF500 FSK l000~700 MHz收发器
- › Microcontrollers Improve Power
- › Micronas最新控制IC优化平板显示器图像质量
- › Micronas 推出FRC 94xyM全高清帧率转换IC
- › Microchip推出新型低成本数字信号控制器系列
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: