Microcontrollers Improve Power
[09-13 17:03:33] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8436次
文章摘要:Microcontroller-based systems typically use a number of peripherals. These range from external UARTs and power-on reset circuitry to watchdog timers. One of the strengths of the 8051 product family is the large number of peripheral functions that are available on-chip. In addition to simplifying a d
Microcontrollers Improve Power,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comMicrocontroller-based systems typically use a number of peripherals. These range from external UARTs and power-on reset circuitry to watchdog timers. One of the strengths of the 8051 product family is the large number of peripheral functions that are available on-chip. In addition to simplifying a design by eliminating components, integrated peripherals also can reduce power consumption. One can assume that the core functionality of any peripheral consumes the same amount of power whether located internal or external to the processor. Locating a peripheral on-chip, however, will eliminate the switching power losses associated with driving an external bus.
Internal Program Memory
Another 8051 feature that is not commonly perceived as a peripheral is program memory. All 8051 derivatives incorporate various amounts of on-chip program memory. This is desired by many system designers as a method of reducing the component count and board area, but it also improves battery life in portable systems. As mentioned previously, this will reduce power consumption by eliminating the need to drive an external bus. There is an additional power savings when using on-chip memory. The 8051 architecture requires the use of a 74373-type latch to demultiplex the lower byte of address. Figure 3 compares the use of internal vs. external program memory. The first uses a DS87C520 High-Speed Microcontroller with a 74AC573 latch and a 27C256 EPROM with an access time of 70ns. The second system uses the same microcontroller, but operating from internal memory. Both systems are operating at 11.0592MHz, executing a short, generic program. From the figure, it is apparent that as much as 49mA can be saved at high frequencies by eliminating the external EPROM and latch from the system.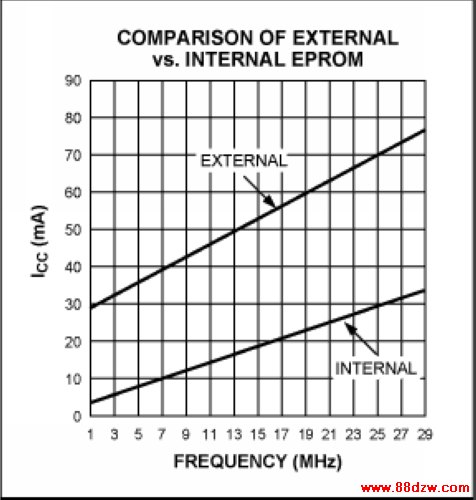
Figure 3. Using internal memory significantly reduces current consumption.
Internal Data Memory
As previously mentioned, the use of on-chip memory instead of external RAM will save power. The enlarged scratchpad of the 80C32 derivatives (256 bytes) is sufficient for stack operations and some data storage in small programs, eliminating the need for external RAM.For designs requiring more data memory or needing to implement an external stack, however, additional SRAM may be required. Although low-power SRAMs are available, their power consumption must also include that associated with a 74373 series latch as well as capacitive losses driving the external bus. This can be mitigated by using devices with expanded on-chip RAM. Figure 4 shows the power consumption of two systems using SRAM mapped into the 8051 MOVX data space. The first uses a DS87C520 high-speed microcontroller with a 74AC573 latch and a DS2064 SRAM. The second system uses the same microcontroller but uses 1Kbyte of internal MOVX data memory. Both microcontrollers are operating at 11.0592MHz, executing a short, generic program that reads and writes to MOVX data memory. From the figure, it is apparent that as much as 9mA can be saved at high frequencies by eliminating the external SRAM and latch from the system.
上一页 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] 下一页
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
《Microcontrollers Improve Power》相关文章
- › MICRF501 300~500 MHz收发器
- › MICRF500 FSK l000~700 MHz收发器
- › Microcontrollers Improve Power
- › Micronas最新控制IC优化平板显示器图像质量
- › Micronas 推出FRC 94xyM全高清帧率转换IC
- › Microchip推出新型低成本数字信号控制器系列
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:Microcontrollers Improve Power
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: