Fan Control Advances: Consider
[09-13 17:03:04] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8926次
文章摘要:Abstract: Controlling fan speed as a function of temperature is a useful technique for reducing system noise and increasing the fan's lifetime. Two different types of integrated circuits (ICs) that can be used to control fan speed are discussed. Brushless DC fan motors can be controlled using a
Fan Control Advances: Consider,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comAbstract: Controlling fan speed as a function of temperature is a useful technique for reducing system noise and increasing the fan's lifetime. Two different types of integrated circuits (ICs) that can be used to control fan speed are discussed.
Brushless DC fan motors can be controlled using a variety of methods. The simplest method is on/off switching with a single transistor. Digitally programmable variable control can be achieved using linear regulators or power op amps combined with DACs or using PC health monitor ICs which offer DACs with an output that can be applied to an amplifier for driving a fan. PWM fan control chips are available that require a DAC for digital interface. Note that PWM methods have to be used with some caution.
The newest developments for fan control are digital interface ICs with complete fan driver circuits, such as the MAX1669, which include everything except for the power transistor. The MAX6650/MAX6651 take the forefront in advanced fan control because these devices are truly fan speed regulators.
The MAX1669 represents the most common type of fan control available, providing either a linear DAC output or a PWM output. It stands out because it includes a remote-junction temperature sensor input that can be connected to ICs equipped with sensing junctions or to bipolar transistors, such as 2N3904s, used as remote sensors. The MAX1669 is especially suited in situations where the fan cannot be equipped with a tachometer output because of either cost or technical requirements. Figure 1 is an example of the MAX1669 used for linear control of a fan.
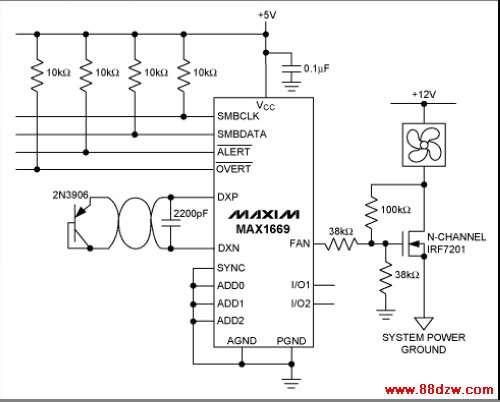
Figure 1. Typical circuit for linear control of a fan using the MAX1669.
Fan Control Problems and Solutions
A big problem in fan control is the nonlinear behavior of the fan with respect to input voltage. As shown in the graph in Figure 2, the typical fan does not even begin to rotate until voltages between 3V to 8V is applied, depending on the fan. And even for a given fan, this exact voltage is subject to variations from fan to fan, and with temperature and age. When using a part such as the MAX1669, with simple fan driver amplifiers or PWM output, fans must be commanded to full speed briefly before programming low speeds. It is difficult to predict, and subject to wide variation, just how low the low speed can be. With lengthy evaluation, a minimum could be found for any fan. No matter what speed the fan is programmed to, this is an open-loop system that does not regulate fan speed.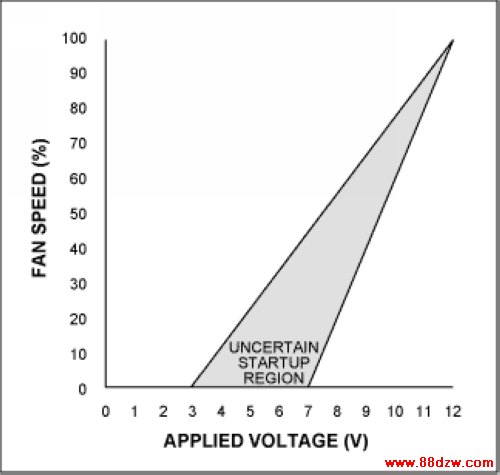
Figure 2. This graph depicts typical fan speed vs. applied voltage.
This lack of predictability of threshold voltages has given birth to some "Rube Goldberg" schemes among some of the fan control ICs. For instance, one IC examines whether or not the fan is rotating, and if it isn't, it raises the drive incrementally. If the fan still isn't rotating it raises it another increment and so on until the fan starts.
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
- 上一篇:改进后的电路图
《Fan Control Advances: Consider》相关文章
- › Rev Up Your Fan Speed Control
- › FANUC6系统的特点及功能,FANUC6系统的硬件
- › FANUC 7系统的硬件结构及软件结构
- › Simple Circuit Activates Fan W
- › HFAN-08.2.0: Thermoelectric Co
- › Fan Control Advances: Consider
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:Fan Control Advances: Consider
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:Fan Control Advances: Consider
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:Fan Control Advances: Consider
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:Fan Control Advances: Consider
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: