Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif
[09-13 17:03:24] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8873次
文章摘要:Figure 3. A user-programmable temperature sensor monitors the temperature of a remote CPU's on-chip p-n junction.Another important feature found on some of these types of sensors (including the sensor shown in Figure 3) is the ability to interrupt a microcontroller when the measured temperature
Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.com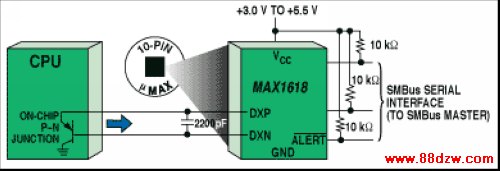
Figure 3. A user-programmable temperature sensor monitors the temperature of a remote CPU's on-chip p-n junction.
Another important feature found on some of these types of sensors (including the sensor shown in Figure 3) is the ability to interrupt a microcontroller when the measured temperature falls outside a range bounded by high and low limits. On other sensors, an interrupt is generated when the measured temperature exceeds either a high or a low temperature threshold (i.e., not both). For the sensor in Figure 3, those limits are transmitted to the temperature sensor via the SMBus interface. If the temperature moves above or below the circumscribed range, the alert signal interrupts the processor.
Pictured in Figure 4 is a similar device. Instead of monitoring one p-n junction, however, it monitors four junctions and its own internal temperature. Because Maxim's MAX1668 consumes a small amount of power, its internal temperature is close to the ambient temperature. Measuring the ambient temperature gives an indication as to whether or not the system fan is operating properly.
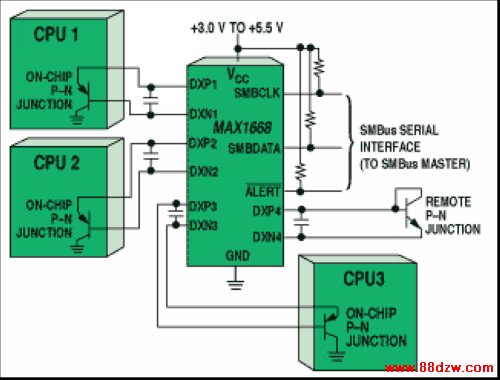
Figure 4. A user-programmable temperature sensor monitors its own local temperature and the temperatures of four remote p-n junctions.
Controlling a fan while monitoring remote temperature is the chief function of the IC shown in Figure 5. Users of this part can choose between two different modes of fan control. In the PWM mode, the microcontroller controls the fan speed as a function of the measured temperature by changing the duty cycle of the signal sent to the fan. This permits the power consumption to be far less than that of the linear mode of control that this part also provides. Because some fans emit an audible sound at the frequency of the PWM signal controlling it, the linear mode can be advantageous, but at the price of higher power consumption and additional circuitry. The added power consumption is a small fraction of the power consumed by the entire system, though.
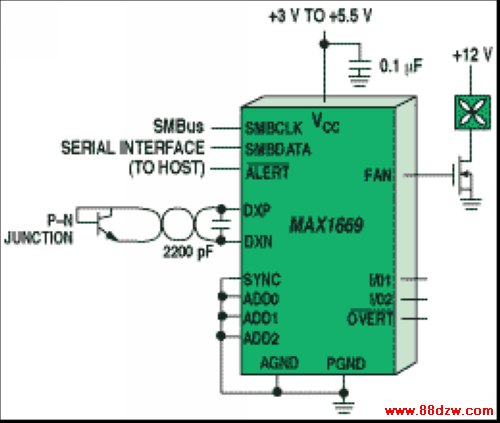
Figure 5. A fan controller/temperature sensor IC uses either a PWM- or linear-mode control scheme.
This IC provides the alert signal that interrupts the microcontroller when the temperature violates specified limits. A safety feature in the form of the signal called "overt" (an abbreviated version of "over temperature") is also provided. If the microcontroller or the software were to lock up while temperature is rising to a dangerous level, the alert signal would no longer be useful. However, overt, which goes active once the temperature rises above a level set via the SMBus, is typically used to control circuitry without the aid of the microcontroller. Thus, in this high-temperature scenario with the microcontroller not functioning, overt could be used to shut down the system power supplies directly, without the microcontroller, and prevent a potentially catastrophic failure.
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
《Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif》相关文章
- › Using Analog Temperature Senso
- › Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif
- › Compact DWDM laser Temperature
- › Measuring Temperature with the
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:Temperature Sensor ICs Simplif
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: