Flexible Fault Protection
[09-13 17:03:08] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8212次
文章摘要:Abstract: A flexible circuit is shown that limits current or removes power in response to a command from the user or other fault-indicating signal. It accommodates manual-reset (MR), over-temperature, and protection in hot-swap applications. Residing on either the backplane/host side or the removabl
Flexible Fault Protection,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comAbstract: A flexible circuit is shown that limits current or removes power in response to a command from the user or other fault-indicating signal. It accommodates manual-reset (MR), over-temperature, and protection in hot-swap applications. Residing on either the backplane/host side or the removable-card/remote-device side of the backplane connectors, it guards against start-up faults when a card or board is inserted into a rack or host with the main power supply turned on.
Many applications require the capability to automatically disconnect power from an operating circuit. Such applications include thermal shutdown of high-voltage power supplies in radar and X-ray systems, shutdown to limit inrush current during power-up or hot-swapping of pc cards, and shutdown to ensure that a card is properly seated before power is applied. In general, a power fault system will keep the power off following the system fault, until it is deliberately reset.
Figure 1 is a flexible circuit that limits current or removes power in response to a command from the user or other fault-indicating signal. It accommodates manual-reset (MR), over-temperature, and interlock-switch inputs. U1, for instance, is a circuit-breaker IC designed to offer protection in hot-swap applications. Residing on either the backplane/host side or the removable-card/remote-device side of the backplane connectors, it guards against start-up faults when a card or board is inserted into a rack or host with the main power supply turned on.
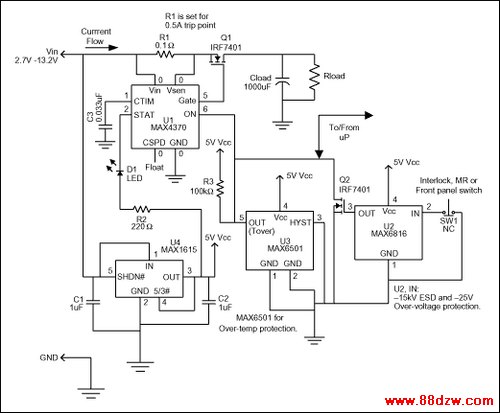
Figure 1. This circuit provides general over-current and over-temperature protection.
Two main fault conditions are possible. Discharged filter capacitors on the card or remote device can provide a low impedance to ground that momentarily collapses the host power supply. Or, a card only partially seated in its connector can generate erroneous data. U1 prevents the first condition by regulating inrush current during a programmable start-up period, allowing the system to stabilize safely. During normal operation, two internal comparators provide short-circuit and over-current protection (DualSpeed/BiLevel capability). The second condition is handled by routing U1's current output (ON) through two pins at the outer edges of the card (Figure 2).
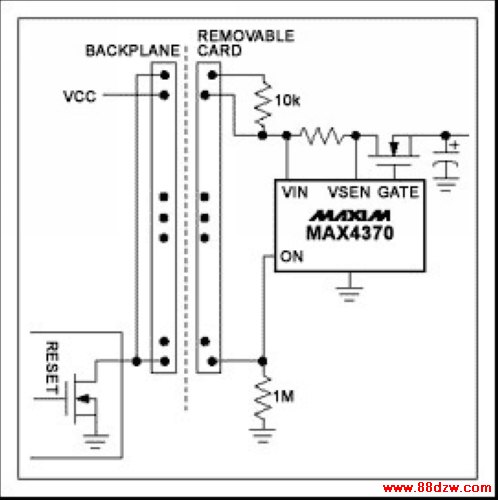
Figure 2a.

Figure 2b.
Figure 2a and 2b. To insure properly seated pc cards on the backplane's card side (a) or host side (b), this IC (MAX4370) routes current through the outer pins of the card connector.
- 上一篇:三相交流异步电动机的拆装
《Flexible Fault Protection》相关文章
- › Flexible Fault Protection
- › 奥地利微电子推出获得FlexRay V2.1 Rev B认证
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:Flexible Fault Protection
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:Flexible Fault Protection
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:Flexible Fault Protection
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:Flexible Fault Protection




 当前位置:
当前位置: