Reference Design for a Class-D
[11-20 17:32:34] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 模拟电子技术 阅读:8343次
文章摘要:As a stereo Class D IC, the MAX9736 also features two integrated op amps at the input. Available to use for general filtering, in this reference design those op amps are used to build a second-order highpass filter for the left/right channels. The op amps have their negative inputs and outputs acces
Reference Design for a Class-D,标签:模拟电子技术基础,模拟电子电路,http://www.88dzw.comAs a stereo Class D IC, the MAX9736 also features two integrated op amps at the input. Available to use for general filtering, in this reference design those op amps are used to build a second-order highpass filter for the left/right channels. The op amps have their negative inputs and outputs accessible, so a multiple-feedback inverting filter configuration is used. C116/C216 are for blocking the DC-input voltage to reduce output offset.
Power Stage
The design features three channels of speaker power amplification. A MAX9736B is configured in stereo mode to drive the left and right speakers, and can provide 2 × 11W into 4Ω. For the third channel, a MAX9736A is configured as a mono subwoofer amplifier.
In mono mode, the two Class D outputs of the MAX9736A are connected in parallel to allow for higher output power. In mono mode the subwoofer channel can deliver 30W into 4Ω (VDD = 19V). The input stage for the subwoofer channel is the same as that used for the left and right channels. After the input stage, the left and right signals are then summed using U5-B to create the mono subwoofer channel. R303 is used to set the subwoofer channel gain at the summing amp.
To enable a maximally flat response down to very low frequencies, the system is configured with a sixth-order filtered alignment for the subwoofer. This approach means that the fourth-order highpass response of the vented speaker is supplemented with a second-order electrical highpass in the active circuitry. U5-C is used to realize the noninverting Sallen-Key, second-order highpass filter for the subwoofer.
This system requires a high Q, which leads to 13dB of boost at 40Hz. To avoid overloading the speaker and amplifier, the Sallen-Key filter is set up to act as a sliding highpass; the filter acts dynamically as the amplifier output reaches its limit. The value of input resistor R305 is designed to reduce automatically (using the opto-coupled FET, U7) to a value so that the filter Q is lowered to 0.5, resulting in no boost at all.
The peak output voltage of the subwoofer amplifier, U2, controls the signal to the opto-FET. D6 and C16 form a peak detector, which senses the output peak level with a fast attack time. The operating threshold for the peak detector can be adjustable or fixed, depending on whether R7 is stuffed or R8/R9 are stuffed. The LED D5 turns on when this control circuit is active.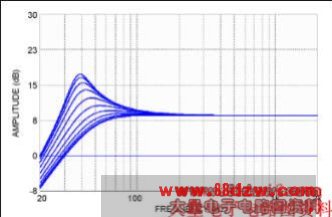
Figure 2. Simulation results of the dynamic bass boost from the subwoofer channel. The Q of the highpass filter is reduced while the cutoff frequency is also increased, as the subwoofer level approaches its limit.
The two op amps built into the MAX9736A are configured into a fourth-order lowpass subwoofer filter that complements the highpass filter used for the left/right channels.
J1 is the power-supply input connector chosen to be a standard laptop-type coaxial socket. A typical laptop power supply has an average output voltage of around 19V and serves as a good power source for the docking system. After some filtering through C1 and C2, the voltage is labelled PV
《Reference Design for a Class-D》相关文章
- › Reference Voltage for Multiple
- › Understanding Voltage-Referenc
- › Reference Design for a Class-D
- › 确保打印头电源动态输出电压的参考设计,Reference D
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:Reference Design for a Class-D
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:Reference Design for a Class-D
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:Reference Design for a Class-D
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:Reference Design for a Class-D




 当前位置:
当前位置: